This article explains, what is SSL Certificate, how it works, types of SSL certificate, and how to stay safe online with help of SSL certificates?
SSL is a file on a host server of a website that works as digital certificate. It enables websites to move from HTTP to more secure HTTPS. SSL make SSL/TLS encryption, they contain public key and identity of website, along with related information. They make sure that all the data transmission done with site remain secure.
SSL certificates are necessary in order to make all the transactions with the website secure and protect user’s information. It prevents hackers and criminals from reading or modifying information transferred between two systems. A website has a padlock icon next to its URL in the address bar, indicating that website you visiting is protected through SSL.
What information does SSL certificate contains?
List of Information that an SSL certificate contains:
- The domain name for which the certificate was used for.
- The person, organization, and device name it was issued to.
- The issuer of the certificate
- Certificate authorities digital signature.
- Associated subdomains.
- Issue date and expiration date of Certificate.
- The Public Key( Private key is kept a secret).
Why do website need SSL Certificates?
SSL(Secure Socket Layer), more commonly called TLS(Transport Layer Security), is a protocol for encrypting Internet traffic and verifying server identity. Any website with an HTTPS web address uses SSL/TLS.
Encryption: SSL certificate enables SSL/TLS encryption using public-private key pairing. Clients (such as web browsers) get the public key necessary to open a TLS connection from a server’s SSL certificate.
Authentication: With help of SSL Certificates client verifies that client is talking to the real owner of domain and correct server. This also prevents domain spoofing and other kinds of attacks.
HTTPS: SSL certificate is required to move a website’s address from an HTTP web address to HTTPS. It is crucial for online businesses because HTTPS websites have their traffic encrypted by SSL/TLS which makes the website more secure.
Normally many users won’t notice the difference between an http:// and an https:// web address, But these days most browser shows HTTP sites as “not secure” in a more noticeable way, providing an incentive for switching to HTTPS and making it more secure from user’s perspective.
In addition to securing user data in transit, HTTPS makes sites more trustworthy from a user’s perspective. Many users won’t notice the difference between an http:// and an https:// web address, but most browsers have started tagging HTTP sites as “not secure” in more noticeable ways, attempting to provide an incentive for switching to HTTPS and increasing security.
How does SSL Certificate Work?
SSL works by encrypting any data transferred between users and websites, or between two systems, making it impossible to read. It uses encryption algorithms to scramble data in transit. This protects user’s data which may include potentially sensitive information such as names, addresses, credit card numbers, or other financial details.
Here is how this process works:
- A browser or server attempts to connect to a website’s server secured with SSL.
- The browser or server requests web server to identifies itself.
- The web server sends the browser or server a copy of its SSL certificate in response.
- The browser or server checks the digital signature of certificate authority in SSL certificate. If signature found right, it signals this to the webserver.
- The web server then returns a digitally signed acknowledgment to start an SSL encrypted session.
- Encrypted data is shared between the browser or server and the webserver.
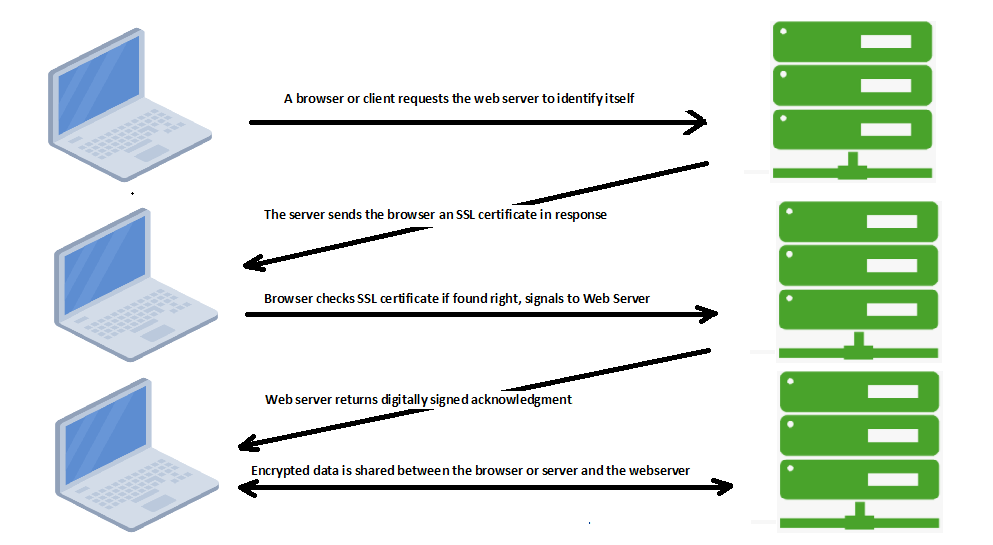
This process is referred as “SSL handshake”.
Types of SSL Certificate
There are different types of SSL certificates with different validation levels. The six main types are:
- Extended Validation certificates (EV SSL)
- Organization Validated certificates (OV SSL)
- Domain Validated certificates (DV SSL)
- Wildcard SSL certificates
- Multi-Domain SSL certificates (MDC)
- Unified Communications Certificates (UCC)
Extended Validation certificates (EV SSL)
This is the highest-ranking and most expensive type of SSL certificate. It is used for high profile websites which collect data and involve online payments. To Obtain this SSL certificate website owner has to go through a standardized identity verification process to confirm they legally own the domain.
Organization Validated certificates (OV SSL)
These SSL certificates are the second most expensive after EV SSLs and are high-level assurance certificates. Website owners are required to give their business documents and proof of domain ownership to get this certificate. This type of certificate also displays the website owner’s information in the address bar. The main purpose of the OV SSL certificate is to encrypt website/business and user’s sensitive information that is being used for transactions.
Domain Validated certificates (DV SSL)
Domain Validated SSL Certificate (DV SSL) comes up with minimal encryption and lower assurance. Website owners only needs to validate their domains by responding to an email or phone call. A single Domain SSL certificate (DV SSL) can secure both www and non-www domains version. Browser address bar only displays HTTPS and padlock. This certificate tends to be used for blogs or informational websites.
Wildcard SSL certificates
A Wildcard SSL Certificate saves you money and time by securing your domain and unlimited sub-domains on a single certificate. Wildcard certificates work the same way as a regular SSL Certificate, allowing you to secure the connection between your website and your customer’s Internet browser – with one major advantage. Wildcard SSL certificates have an asterisk * as part of the common name, where asterisk represents any valid sub-domains that have the same base domain.
For example a single Wildcard certificate for *.website.com can be used to secure:
- payments.yourdomain.com
- login.yourdomain.com
- mail.yourdomain.com
- download.yourdomain.com
- anything.yourdomain.dom
Multi-Domain SSL Certificate (MDC)
Multi-domain certificates (MDC) allow you to secure many domains and/or sub-domain names. Consolidate your SSL management process and manage the SSL encryption for all of your domains under just one SSL certificate for multiple domains.
For example:
- www.example.com
- example.org
- mail.this-domain.net
- example.anything.com.au
- checkout.example.com
- secure.example.org
Multi-Domain certificates do not support sub-domains by default. If you need to secure both www.example.com and example.com with one Multi-Domain certificate, then both hostnames should be specified when obtaining the certificate.
Unified Communications Certificate (UCC)
UCC SSL Certificate stands for Unified Communication certificate. It is designed to protect multiple fully qualified domains (FQDN) under single SSL management. Under UCC SSL, the first domain is considered ‘Primary Domain’ or ‘Base Domain’ and other domains are regarded as SAN (Subject Alternative Names) domains.
By allowing users to protect multiple domains, saves time in managing SSL and lowers the cost as well. In the case of the Organisation validation option, it is required to give business documents to CA and takes up to 3 days where Certificate with domain validation no document is required, and the certificate is issued within few minutes.
How SSL certificates are obtain?
Websites need to obtain their SSL certificate from a certificate authority(CA). CA is a trusted third-party organization, that generates and issues SSL certificates.
Obtaining your SSL involves the following steps:
- Complete your server set up and submit your website details to the certificate Authority, make sure details like company name and address, etc. are correct.
- Generate Certificate Signing Request(CSR) on your server with help of your hosting company. Submitting this to the Certificate Authority to validate your domain and company details
- After the Certificate authority issue the certificate, it needs to be installed and activated on the website’s origin server.
- Once activated on the server website will able to load over HTTPS and all traffic to and from the website will be encrypted and secure.
How to stay safe online?
Although SSL certificate guarantees secure transmission of data between your browser to websites server, it does not guarantees that website you’re visiting is safe. Even hackers can create website and get SSL certificate. Sometimes hackers create site that mimics large brands and scams online users. Here are list of things you can do to stay safe online:
To avoid these kinds of attacks:
- Check if domain name of the site you visiting is spelled correctly. The URL of a fake site might differ by only one character – e.g., amaz0n.com instead of amazon.com. If you have any doubt, search the name of the site you intended to visit directly.
- Never enter logins, passwords, banking credentials, or any other personal information on the site unless you are sure of its authenticity.
- You should consider whether you believe in the product and prices a site is offering you, before registering in the site.
- Make sure your devices are well protected, use a good anti-virus for your PC and phone.
Cyber security risks continue to grow. Therefor it is important to understand which type of SSL certificate is best suited for your website. It also important to spot and avoid unsafe website. Keeping all these points in mind can helps internet users can stay safe from potentially dangerous sites, avoid scams and protect their personal data from cyber criminals.

